Two previous posts covered some core labor markets data for the U.S.:
Here, let's take a look at the weekly (higher frequency) data unemployment claims.
First, initial unemployment claims, with data coverage through the week of October 17th:
The above chart shows 1-month cumulative initial unemployment claims, smoothing some of weekly volatility in the series.
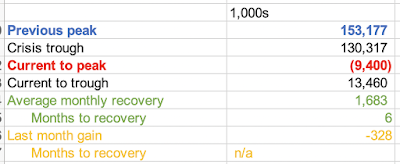
Current reading stands at 3,194,750 which is above the 2008-2011 crisis peak of 3,169,786 and only slightly below all-time pre-COVID19 high of 3,313,000 attained in January 1975.
In absolute level numbers, preliminary first-time claims for the week of October 17, 2020 stand at 756,617 which is still 3 times the rate of first-time claims filings in the last week before COVID19 pandemic onset (March 14, 2020). The good news is, preliminary estimate for the new claims for the week of October 17 suggest a decline in new claims filings of 73,125 on week prior - the fastest rate of reductions in 10 weeks. However, overall average weekly decline in first-time claims over the last 10 weeks has been rather unimpressive at 8,212. At this rate of improvement, it will take almost 62 weeks to draw current first-time claims down to the levels seen in the last pre-COVID19 week.
In line with the crisis timing, average duration of unemployment is climbing up, too:
Based on monthly data through September 2020, average duration of unemployment is about to hit pre-crisis average in October. This sounds like a good thing, until you realise that the duration of unemployment fell to historically low levels as COVID19 crisis unfolded because of the unprecedented rate of jobs losses and unemployment claims increases (see net chart below). It remains to be seen how it will behave in months ahead.
Past three recessions have been associated with increasing average duration of unemployment through recovery periods. They have also been associated with longer periods of elevated duration. In fact, in the last three recessions, average duration of unemployment never reached pre-recession levels, implying that long-term unemployment got worse in every recovery period since 1990 on. If this trend is consistent with the COVID19 recession, U.S. long term unemployment duration will rise once again.
For the last chart, consider employment index dynamics though September 2020:
Despite the headline 'historically fast' recovery, actual employment remains in dire state, with current dynamics through September 2020 indicating the third worst employment performance in the history of the modern economy. Based on the 3-months average gains in seasonally-adjusted employment, it will take us another 8 moths before we regain pre-crisis peak employment levels, implying the 5th fastest recovery in employment in history. Based on September rate of improvement, the process will take another 16 months, which would make the current recovery the fifth slowest on record. Based on the dynamics of change in the jobs recovery since May 2020, we can expect the jobs recession to last 45 months, which would make it the 3rd worst recession in history. So far, the average rate of decline in the jobs gained per month during the recovery is 15% per month.
In the Great Recession, it took the economy 76 weeks to recover from trough of the recession to pre-recession peak employment. The average monthly rate of recovery from the trough until regaining pre-recession peak was 0.128% per month. This would put the month when we would recover from the COVID19 pandemic to July 2025, making the COVID19 pandemic a second worst recession in history after the Great Recession.