In the previous two posts I looked at Q2 national accounts for Ireland in terms of headline GDP and GNP figures, y/y and q/q changes in the first post; and half-yearly figures analysis in the second post. The headline conclusion was that:
- Q2 2013 real (constant prices) GDP performance is weak, but posits some growth, pushing us out of official third dip recession.
- Irish real GNP fell 0.1% in Q2 2013 compared to Q2 2012, having only marginally reversed the 6.01% y/y rise recorded in Q1 2013.
- Broadly-speaking, H1 figures show continued economic performance within the new structural range of slower economic activity that set on with the 'recovery' of H2 2010 (the Celtic Canary period).
- Crucially, moving to less volatile half-yearly figures, Y/Y Irish real GDP fell 1.10% in H1 2013, marking a second consecutive 6-months period of declines (it was down y/y 0.75% in H2 2012 as well).
- Y/Y Irish real GNP rose 2.87% in H1 2013, marking third consecutive 6-months period of increases in GNP.
- At current rates of growth (that is taking 3-year average, since current annual rate is negative), it will take us until 2029 before we can reach real levels of GDP consistent with the pre-crisis levels.
Now, let's take a look at the underlying components of GDP and GNP from the expenditure side of the national accounts. Since we have half-yearly data, we might as well focus on longer-term, more stable series. For this purpose, let us also look at nominal (not real) values, so we have some idea as to actual activity on the ground, reflective of price changes, as well as volumes changes. There are several reasons for doing this:
- Nominal values, expressed in current prices are actually linked to what we get paid, what we pay for and what the economy produces;
- Nominal values are also reflective of what the Government spends, collects and what the potential for debt servicing is when it comes to economy's output; and
- Nominal values are free from the impact of the inflation adjustments, which are made based on 'average' households and firms, rather than on what we do observe in the economy itself.
There are drawbacks to this analysis, so like everything else in economics, this is not intended to be 'completely and comprehensively' conclusive.
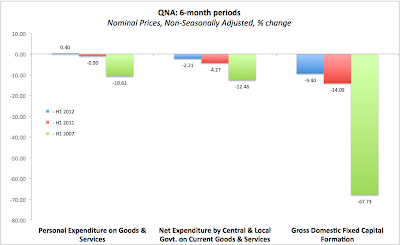
As can be seen from Chart above, Personal Expenditure on Goods and Services rose 0.4% y/y in H1 2013 - which is good news. However, the same was down on H1 2011 (recall that the Government is keen on claiming that consumer confidence and consumption spending rose during its tenure, which is obviously contradicted by the data we have). Compared to peak pre-crisis performance (peak referencing output peak, not specific series peak), we are down 10.61% on H1 2007.
Understandably, Government spending (net of tax receipts) is down when it comes to current goods and services (as opposed to capital goods and services): -2.11% on H1 2012, -4.27% on H1 2011 and -12.46% on H1 2007. You might think this is 'huge', but y/y over the first 6 months of 2013 our net current Government spending is down only EUR 278 million and when it comes to vast/deep cuts since 2007, H1 2007 spending was cut EUR1,754 million by the end of H1 2013.
Meanwhile, Gross Fixed Capital Formation (basically investment in the economy) is down 9.40% in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012, down 14.09% compared to H1 2011 and down 67.73% compared to H1 2007. The reductions in capital investment jun H1 2013 compared to H1 2007 are ten-fold the size of reductions in current Government spending at EUR17,542 million. For another comparison, reductions in personal expenditure on goods and services by households over the same period is EUR4,757 million.
Put in different terms, domestic economy is still falling, with no stabilisation in sight.
Next: external trade and GDP & GNP series:
Exports of goods and services - the only part of the economy that was booming (+15.94% in H1 2013 on H1 2007 and +5.44% on H1 2011) are hitting some bumps. H1 2013 posted a decline in total exports of 0.67% y/y. Meanwhile, imports of goods and services were up 0.08% y/y. As the result of this, our trade balance fell 2.32% y/y in Q2 2013 and is down 3.15% y/y for H1 2013. This is not good, as key Exchequer projections and debt sustainability analysis require healthy growth in trade surplus, not a decline. But more on this below…
GDP at current prices fell 1.49% in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012 and is down 0.28% on H1 2011 and down 15.26% on H1 2007. Recall that our real GDP fell 1.10% y/y in H1 2013. In other words, there is no growth in actual underlying activity. This is pretty bad. Actual euro notes we have in the economy's 'pockets' at the end of H1 2013 (as imperfectly measured by GDP) were fewer than at the end of H1 2012 and H1 2011. And these fewer euros were not worth more, either. I wouldn't call this 'stabilisation'.
Net factor income outflows abroad are falling as well and I commented on these in the previous posts.
GNP expressed in current market prices is 2.32% ahead in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012 and 2.92% ahead of H1 2011. This is good news, especially since GNP is a more accurate reflection of our real economy's output (also rather imperfect) than GDP. Not so good news: GNP is still down 17.53% on H1 2007.
Chart below drills into the composition of our external trade:
The above clearly shows the massive swing of our external trade activities from goods sectors to services sectors. And on imports of goods side it shows the legacy of the consumption bust, which remains one of the two largest drivers for improved external trade statistics we see on national accounts.
Finally, total domestic demand: the measure of the economy that covers all domestic activities of private and government consumption and investment combined, plus chafes in stocks.
As the above shows, domestic economy continues to suffer losses in activity: Total Domestic Demand fell 0.95% in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012 and is down 3.05% on H1 2011. Compared to H1 2007, Total Domestic Demand is down 27.41%.
Summary: Bad news: Despite improvements in real variables in Q2 2013, domestic economy continued to contract in H1 2013, with domestic demand down compared to H1 2012, driven by declines in Net Government Current Expenditure and in Gross Fixed Capital Formation. Good news is that decline in domestic demand was ameliorated by a marginal increase in Personal Expenditure on Goods and Services. On the bad news side, exports of goods and services fell in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012. These changes, together with domestic demand movements resulted in GDP falling in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012. Lower rate of profits repatriation out of Ireland by the MNCs has resulted in an increase in GNP in H1 2013 compared to H1 2012.
In simple terms, if Irish economy were a student asking for a report card for H1 2013, I don't think there would be much on it worth boasting about. Let's hope H2 2013 will be different for the better.