Remember them?
One of Europe's largest banks? Check. The oldest bank in the world with continued trading since 1472? Check. The first bank in history to require a sovereign rescue? Check. In 1624, the Medici Grand Duke of Tuscany rushed to guarantee the deposits of a bank at a time of economic crisis. The only bank in known history that has been bailed out at least five times and nationalised at least twice? Check.
Yep, right, we have the new old news from Italy's Banca Monte dei Paschi di Sienna. Just two and a half years after the last Government rescue in 2017 MPS is now rumoured to need another capital injection: https://www.reuters.com/article/italy-banks-monte-dei-paschi/rpt-update-1-monte-dei-paschi-ceo-tells-board-bank-faces-2-bln-euro-capital-gap-source-idUSL1N2HP0EV.
The latest capital call is a mixture of the residual problems from the, yes, now more than a decade-old (hew, what's decades for MPS, right?) financial crisis and the fresh blows to thee Italian (and European) banks from the pandemic.
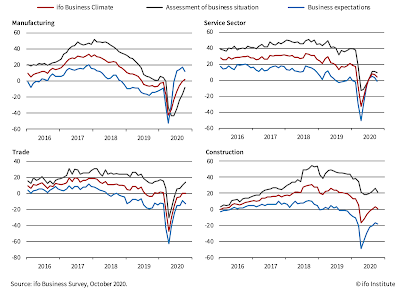
Overall, major European banks have been increasing their capital cushions in thee early stages of the pandemic (https://www.spglobal.com/marketintelligence/en/news-insights/latest-news-headlines/europe-s-top-banks-bulk-up-capital-cushions-but-market-wary-as-virus-resurges-60666650). And, so far, losses in most banks have been either mild or inexistent, and most certainly well below the original (1Q 2020) expectations (https://www.ft.com/content/4d9ee2a0-8e44-4091-b6b7-ca9302f0f314). But banks are losing capital in bucketloads (https://o.canada.com/financial-times/global-banks-lost-nearly-us1-trillion-in-market-value-in-the-pandemics-first-wave-and-theres-another-one-coming/wcm/fe7ab3c9-3681-4703-9833-91a9baf71796) and losses recognitions cannot be delayed for too long (https://www.euromoney.com/article/27ohbp85c1ossyw7im1og/capital-markets/the-road-ahead-europes-banks-face-limited-options-as-they-cope-with-covids-aftermath).
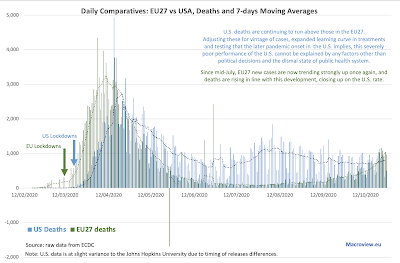
All in, with the second wave of the pandemic raging across the EU, MPS's latest problems are probably just an early warning signal for the rest of the Eeuropean banking sector.