This is an unedited version of my Sunday Times article from January 26, 2014.
Ninety five years ago, in his book The Economic Consequences of Peace (Chapter VI, pg.235-236), John Maynard Keynes observed that "By a continuing process of inflation, governments can confiscate, secretly and unobserved, an important part of the wealth of their citizens."
This week's announcement of price hikes by VHI serves as a timely reminder of the salience of Keynes' analysis. As are the CSO release of comparative data for the cost of living and income per capita for Ireland and the rest of the EU.
The former shows the extent of the ongoing confiscation of households’ wealth through targeted price increases – a core feature of Irish response to the crisis. The latter highlights the combined effects of inflation and income declines on Irish consumers. In 2012, Ireland was the fifth most expensive state in the European Union in terms of the cost of final consumption by private households. At the same time, Irish per capita pre-tax national income, adjusting for purchasing power differentials, was only 11th in the EU.
Irish recovery from a deep fiscal and financial crisis has been a tale of financial repression. Since 2008, our successive Governments have underwritten the status quo of inefficiencies in public services, as well as the cost of recapitalizing the failed banks using the sweat and blood of Irish consumers and taxpayers. As a by-product of this, the state transferred vast amounts of wealth and income from the Middle Ireland and the less well-off households to state-protected and often state-owned producers of goods and services.
Significant parts of these transfers took form of targeted inflation.
Per CSO data, released earlier this month, average annual consumer inflation in 2013 fell to just 0.5 percent, less than one quarter of the average annual inflation recorded in 2011-2012. However, underlying these figures, there is a growing disparity between price trends in the sectors dominated by the state and the sectors where private enterprises compete directly for consumer demand. Not surprisingly, the highest inflation over 2013 was recorded in state-priced and state-owned sectors, such as Education, where prices rose more than nine times faster than across the whole economy.
Looking at the longer-range data reveals an even greater divergence between the state-controlled and market prices. Since the beginning of 2008 through December 2013, aggregate consumer prices rose by slightly more than 3 percent in cumulative terms. Over the same period of time, state-controlled prices were up 22 percent. These sectors cover goods and services that account for around one third of all household consumption in Ireland. Meanwhile, private sectors prices are up only 0.2 percent.
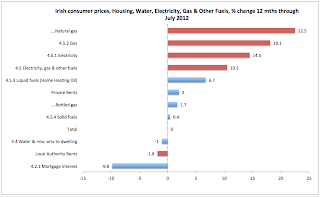
Take the Housing, Water, Electricity, Gas and Other Fuels category, where cost of services to Irish consumers, on aggregate, fell 3.7 percent between 2007 and 2013. This decline was driven by a 25 percent drop in Mortgage Interest costs and 13 percent decline in Private Rents. Costs also fell across virtually all maintenance and repair services associated with housing. In contrast, Local Authority Rents and state-controlled gas prices rose almost by one fifth over the same period. Cost of electricity was up 26 percent. All state-controlled or regulated prices within this group are on the rise, with majority posting double-digit inflation. Price inflation in the energy sector is now so far divorced from underlying costs that a single new entry into the market by Energia is expected to drive prices down by some EUR 300 per annum, potentially erasing two thirds of the price hikes introduced over the last two years.
None of the above services, however, come close to the rampant inflation in Health and Education.
Since the onset of the crisis, costs of Hospital Services in Ireland rose more than 36 percent, over three times the rate of inflation for Outpatient Services. The very same policies that purposefully drove up the cost of Hospital Services are also responsible for a whooping 117 percent cumulative rise in Health Insurance costs since 2007. These policies forced health insurance purchasers to cover the shortfalls in funding available to the HSE, despite the fact that their insurance premiums and general taxes already fund state healthcare. As the result, the cost of health insurance rose at more than three and a half times the rate of inflation in home insurance costs and eleven times faster than inflation in motor insurance.
Tertiary education charges are up 60 percent since 2007. Private-sector dominated secondary and vocational education services meanwhile saw costs rise at roughly one third of the rate of inflation registered in our ITs and universities.
Based on CSO-estimated weights of different goods and services in a standardized consumer basket, inflation in controlled sectors is responsible for confiscating, using Keynes’ terms, just over 10 cents out of every euro spent on consumption of goods and services by an average household in Ireland since the beginning of the crisis. CSO and IMF reported producer prices and international exchange rates and inflation comparatives show that majority of these losses had nothing to do with increased costs of raw materials, intermediate goods and capital used in production. Put simply, they represent a crisis levy designed and imposed by the State and its semi-state companies.
Grim as they are, official inflation statistics, however, tell only a part of the story of wealth destruction imposed onto Irish consumers.
The above costs of inflation are compounded by the declines in Irish households’ disposable incomes due to various tax measures since 2008, combined with decreases in earnings and working hours. All in, Irish households’ today have around 12-15 percent lower disposable incomes than prior to the crisis. Factoring in the effects of unemployment and inflation, in terms of real purchasing power, Irish households are now down some 28 cents on the euro since the beginning of the crisis. Only around 2 cents of this decline is due to private sectors’ inflation with the rest taken up by changes to taxes, regulatory and pricing policies, plus by the monopoly power awarded to state-protected sectors.
Real Ireland - our lower-, middle and upper-middle classes - is paying the full price of the banking, fiscal and economic crises. Meanwhile, the State elites - senior public sector and semi-state officials, managers, politicians, state services executives and affiliated professionals - are ripping the benefits in form of jobs security, pensions and quality of life.
The economics of state confiscation of income through inflation and taxation do not end there, however. The real impact of these measures of financial and fiscal repression can only be dealt with in the context of their distribution across various households and demographics.
Normally, in response to price changes, consumers have an option to alter their demand for goods and services. In the case of ordinary consumption goods, this means that we switch away from more expensive alternatives. Overtime, adjusting for quality of supply, our demand favors lower cost producers and suppliers, who gain market shares at the expense of more expensive, less-efficient ones. Thus, more elastic or more responsive demand helps not only to offset the painful costs of inflation in the short run, but also engenders innovation and competition in the longer term.
For example, during the current crisis, Irish consumers showed strong willingness to opt for discount stores when it comes to shopping for groceries and basic household items. Per latest reports from the retail sector, this Christmas, Tesco’s share of the Irish groceries markets shrunk by 6.2 percent at the expense of Aldi and Lidl which increased their share of the Irish market by double digits. A by-product of this is that the discounters are now offering increasingly more goods tailored to Irish tastes and are widening the breadth of offers in their stores across various segments of consumers. Another upside is that indigenous Irish competitors, such as SuperValu, are gaining the ground in this competition.
In contrast, consumers have little choice in switching away from the state-controlled or monopolised sectors. In 2013, Water Supply and Miscellaneous Services prices were up 64 percent on 2003 levels. More price hikes will come once Irish Water starts issuing charges under the state license to raise prices unabated for the first six years. All without any alternative of a different supplier being available to consumers.
Indirect effects of inflation are also stronger for consumers of goods and services with habitual or long-term demand. Healthcare and education are multi-annual commitments with little room for changing consumer behaviour in response to prices. Patterns of transport demand, linked to choices of location where one lives, are also less responsive to price changes, offering few options for trading out of the adverse effects of inflation. In all of these sectors, consumers have no choice but to pay for price increases. Demographically, younger households, usually heavily indebted via mortgages and struggling financially are the prime targets of this inflation.
Keynes had more to say about the role inflation pays in destroying households’ wealth and income. “… By this method [of inflation, the Governments] not only confiscate, but they confiscate arbitrarily; and, while the process impoverishes many, it actually enriches some. The sight of this arbitrary rearrangement of riches strikes not only at security, but at confidence in the equity of the existing distribution of wealth."
In the case of Ireland during the current crisis, all of the above rings true, save for one important correction: Irish state-sanctioned inflation confiscates wealth and income by transferring money from productive private savings, investment, and consumption to shore up inefficient and often wasteful state services and semi-state sectors. There is little that is arbitrary in the context of the Rip-off Ireland ca 2014.
Box-out:
"You cannot corral a company to go to a particular part of the country unless it will make sense for their business ‐‐ particularly when the company's alternative location may be Amsterdam, Barcelona or Munich”. With these words the IDA spokesperson this week explained why agency-supported multinationals have been largely staying out of the regions, while flocking into Dublin. IDA made a perfectly valid point. Manufacturing exports, even stripping out patent cliff-hit pharmaceuticals, are barely expanding. Remote back office services – the bread-and-butter of so-called ‘call centres economy’ – are on decline across the advanced economies. This leaves what economists call human capital-intensive sectors – the ones largely dominated by jobs for highly-educated 22-35 year-olds coming choosing Ireland as their career stop-over. Working for Google, Facebook, Twitter and other internationally networked globally-trading multinationals, these employees do not want to live in the suburbs, let alone move to the countryside. They require cultural, social and economic amenities of large cities. Whether we like it or not, the MNCs of the 21st century inhabit the world where human capital defines productivity growth, profitability and value added. Bricks and mortar attractions of an IDA Park somewhere in the middle of nowhere do not. Time to bin Bertie’s Era Spatial Development Plans and to think how to transition our regional economic development model to a new and more sustainable basis.