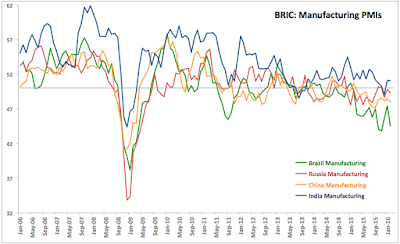
BRIC manufacturing sector conditions have posted major deterioration in February 2016 compared to January, marking another ugly month for world’s largest emerging economies.
Russian Manufacturing PMI for February posted a rather unsurprising and relatively mild deterioration from already marginally-recessionary reading in January. Details are covered here: http://trueeconomics.blogspot.com/2016/03/2316-russia-manufacturing-pmi-february.html.
Chinese Manufacturing PMI continued to tank in February, with country Manufacturing sector remaining the weakest of all BRICs, save Brazil, every month since July 2015. The details are covered here: http://trueeconomics.blogspot.com/2016/03/2316-china-manufacturing-pmi-february.html.
Meanwhile, Brazil’s manufacturing recession “extended to February, with a further drop in incoming new work leading companies to lower production and cut jobs again. Such was the extent of the downturn that firms shed jobs at the second-fastest pace since April 2009,” per Markit.
Brazil’s Manufacturing PMI fell from an ugly 47.4 in January to a horrific 44.5 in February, marking 13th consecutive sub-50 reading. On a 3mo average basis, Brazil’s Manufacturing remained in a contraction (45.8) over the 3mo period through February 2016, just as it was in the contraction (44.0 average) in the 3mo period through November 2015. In 3mo period through February 2015, PMI averaged 50.2.
Per Markit: “Amid evidence of an increasingly fragile economy and a subsequent fall in demand, the level of new business received by Brazilian manufacturers decreased in February. Having accelerated to the fastest since November 2015, the pace of contraction was steep. As a consequence, companies scaled down output again. Production dipped at a sharp and accelerated rate.
Supported by the depreciating real, new foreign orders for Brazilian manufactured goods improved for the third straight month in February. That said, new business from abroad increased at a modest pace overall.”
All in, Brazil remains BRIC’s weakest economy in Manufacturing sector terms every month since February 2015.
As in previous months, India was the only BRIC economy with Manufacturing PMI reading above 50.0 marker. In February 2016, Indian Manufacturing PMI stood at 51.1, unchanged in January 2016. The positive impact of this, however, is weak, at 51.1 marks relatively low (by historical comparisons) growth in the Indian Manufacturing sector.
Per Markit: “Manufacturing business conditions in India continued to improve, with new orders, exports, output and purchasing activity all rising in February. However, a faster expansion in new business inflows failed to lift growth of output and workforce numbers were left broadly unchanged again. PMI
data also highlighted a weaker rise in costs and the first reduction in selling prices since September 2015… Reflecting sustained growth of new work, Indian manufacturers raised their production volumes in February. That said, the rate of expansion eased since January and was marginal overall.”
On a 3mo MA basis, Indian Manufacturing PMI averaged 50.4 in 3 months through February 2016, down on 50.7 average for the 3mo period through November 2015 and down massively on 52.9 3mo average through February 2015.
Overall, India remains the best performing economy in the BRIC group, even though its Manufacturing sector growth is now in slow growth mode since September 2015.
In summary, in February, BRIC group of world’s largest emerging markets economies has posted another deeply disappointing performance across the Manufacturing sector. This compounds adverse headwinds in these economies in January and signals strong possibility of the BRICs exerting a significant negative pressure on global growth.