For those of you who missed my article in yesterday's
Sunday Times, here is an unedited version of it, as usual:
This week marked a new low for the euro zone. Despite all the posturing by Brussels officials about Greek deficits and the incessant talking up of the euro by the ECB and the Commission, the events clearly show that the common currency is lacking credible tools to bring order to public finances of its member states. Thanks to the clientilist politicians and the electorate, keen on piling up debt to pay for perks and inefficient public services, the Greeks really blew it. Then again, given their performance over the last fifteen years – inclusive of massive persistent deficits and outright manipulation of official data to conceal them – about the only surprising thing in the ongoing Greek tragedy is that their bonds are still trading at all.
Much more interesting events, related to the Greek debacle, are unfolding in Ireland. Boosted by the factually erroneous, yet ideologically pleasing statements by international observers, Ireland’s image in the euro area has improved significantly since the publication of the Budget 2010.
Which, of course, is out of line with economic reality on the ground. Far from exiting the PIIGS club of sickest euro economies, comprised of Portugal, Ireland, Italy, Greece and Spain, we are now looking like a country to which the wrath of international bond markets might turn next, once Greece is dealt with.
Let me explain.
This week, writing in the Financial Times, a respected economist, Nouriel Roubini has clearly shown just how escapist is the current thinking about the state of public finances in Ireland.
"The best course [for Greece] would be to follow Ireland, Hungary and Latvia with a credible fiscal plan heavy on spending cuts that government can control, rather than tax hikes... This approach is working in Ireland – spreads exploded as public debt ballooned to save its banks, but came back in as public spending was cut by 20 percent."
Professor Roubini’s comment was echoed later in the day by ECB’s President Jean-Claude Trichet who lent unprecedented amount of good will to the ‘right policy choices’ made by Ireland.
Even our Department of Finance has not, officially, claimed such a thing.
First off - Irish fiscal adjustments from the beginning of the crisis to-date are split approximately 50:50 between higher tax burden and ‘savings’. This debunks Professor Roubini’s general analysis of our policies.
But more importantly, it shows that our Government policies have focused on providing fiscal and financial supports to a select few at the expense of the entire economy. Some €70 billion plus of real future taxpayers’ money has been already committed and €10-15 billion more is still waiting to be deployed post-Nama to rescuing Irish banks’ bondholders. Slightly less comfort was given to the developers who will get a three year holiday on loans repayments courtesy of the taxpayers.
In a real world, economic recovery can only start with ordinary households and businesses. In Ireland, public policy assumes that raising taxes and charges at the times of shrinking incomes and revenues to sustain banks bondholders and narrow interest groups within this society passes for ‘doing the right thing’.
International observers might overlook this fact. For them the costs of encountering a deep and prolonged Irish recession are nil. But for us, the spectre of the 1980s is painfully evident.
In contrast to Greece, Ireland has been hit by an unprecedented, in magnitude and duration, economic recession. Our house prices bust and financial assets collapse was deeper than that of Greece. We also are facing a much more severe banking crisis and a significantly more dramatic rates of deterioration in public deficits. Ditto for our unemployment levels and credit contraction rates.
Our sole claim to better health is a substantially lower existent public debt burden. Alas, this too is optical. In real per capita terms, total levels of debt in Ireland (combining public and private debts) are several times greater than those in Greece.
Even when it comes to budgetary adjustments – as far as Governments plans go – the Greeks are ahead of us. Starting from marginally higher deficit in 2009, the Greeks are planning to bring their deficit to within 3% of GDP limit by 2012. We are planning to do the same by 2014. Of course, both plans are unrealistic, but whilst the EU Commission will attempt to force the Greeks to comply with their target, no one will be closely monitoring our Government’s progress.
In summary, we are nowhere near exiting the PIIGS club.
But let’s take a look at the ‘Love the Irish Policies’ media circus going on in international press. Contrary to Professor Roubini statement, Irish Government has been unable to achieve meaningful cuts in public spending to-date. Instead, we delivered a reallocation of some funding from one side of public expenditure to another. ‘Cuts’ in majority of departments have been simply re-diverted to social welfare and Fas.
By Government-own admission, there will be no net reduction in public expenditure in Ireland since 2009. Department of Finance’s "Ireland – Stability Programme Update, December 2009" provides some stats. In 2009, Gross Current Government Expenditure in Ireland stood at €61,108 million. In 2010 it is budgeted to reach €61,872 million. The latter figure does not include the cost of recapitalizing the banks post-Nama. In 2011-2014 the Government is projecting the Gross Current Expenditure to rise steadily from €63,518 million to €65,768 million.
To Professor Roubini this might look like savings, but to me it looks like the Government continuing to leverage our economic future in exchange for avoiding taking necessary medicine now.
The only reasons why our deficits are expected to contract from 2011 through 2014 is because the Government has been slashing public investment, raising tax burden and is banking on a robust recovery after 2010.
Overall, DofF plans for a 2.8% cut in the General Government Balance in 2010, and that will leave us (per their rosy forecasts on growth and tax revenue) at 11.6% deficit relative to GDP, down a whooping 0.1 percentage point on 11.7% deficit achieved in 2009. Adding expected costs of banks recapitalization, our Government deficit can easily reach beyond 14-15 percent of GDP this year. Greece is now aiming for 8-9% deficit this year under a watchful eye of the Commission. Do tell me Budget 2010 qualifies us for being treated as a stronger economy than Greece.
Stripping out its interest rate bill, Greece is planning for lower per-capita state borrowing in 2010 than Ireland. But Irish Exchequer is planning to raise its borrowing this year by 3%. If international observers are correct, why would the Government that managed to cut its spending by 20% increase its borrowing? That would only make sense if the revenue is expected to fall by more than 20%. Yet Budget 2010 assumes tax revenue decline of only 4.7% in 2010 and an increase in non-tax revenues.
So what has Irish Government done to deserve such a sweet-heart treatment from the EU and Professor Roubini?
One word comes to mind – smart marketing. Budget 2010 simply took €4,051 million from one Government pocket and loaded it into another. Then, the Government promptly reversed itself out of some of the higher profile cuts, such as those imposed on higher earners in the public sector. Even at the highest point of estimates, the savings – before they get cancelled out by rising spending and falling revenue – amount to the total of 6.42% of the Gross Total Expenditure in 2009.
After 2 years of the deepest economic crisis in the euro area, we are now facing one of the heaviest upper marginal tax burdens in the developed world, and a deficit that is simply out of control. Hardly the road map to a recovery.
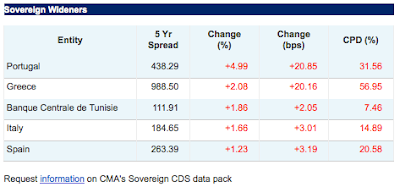 Makes you wonder if Portugal, Italy and Spain bonds brokers have been pushing their clients into losses as hard as our own did...
Makes you wonder if Portugal, Italy and Spain bonds brokers have been pushing their clients into losses as hard as our own did...


















































